India has been actively making efforts to confront climate change, with various initiatives aimed at mitigating its impact and building resilience against environmental challenges. The country, being one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases, understands the urgency of addressing the pressing issues related to climate change.
Despite the challenges, India has taken concrete steps to combat the effects of rising temperatures, unpredictable weather patterns, and environmental degradation. In this light, the Indian government has been implementing policies that aim to reduce carbon emissions and boost renewable energy sources.
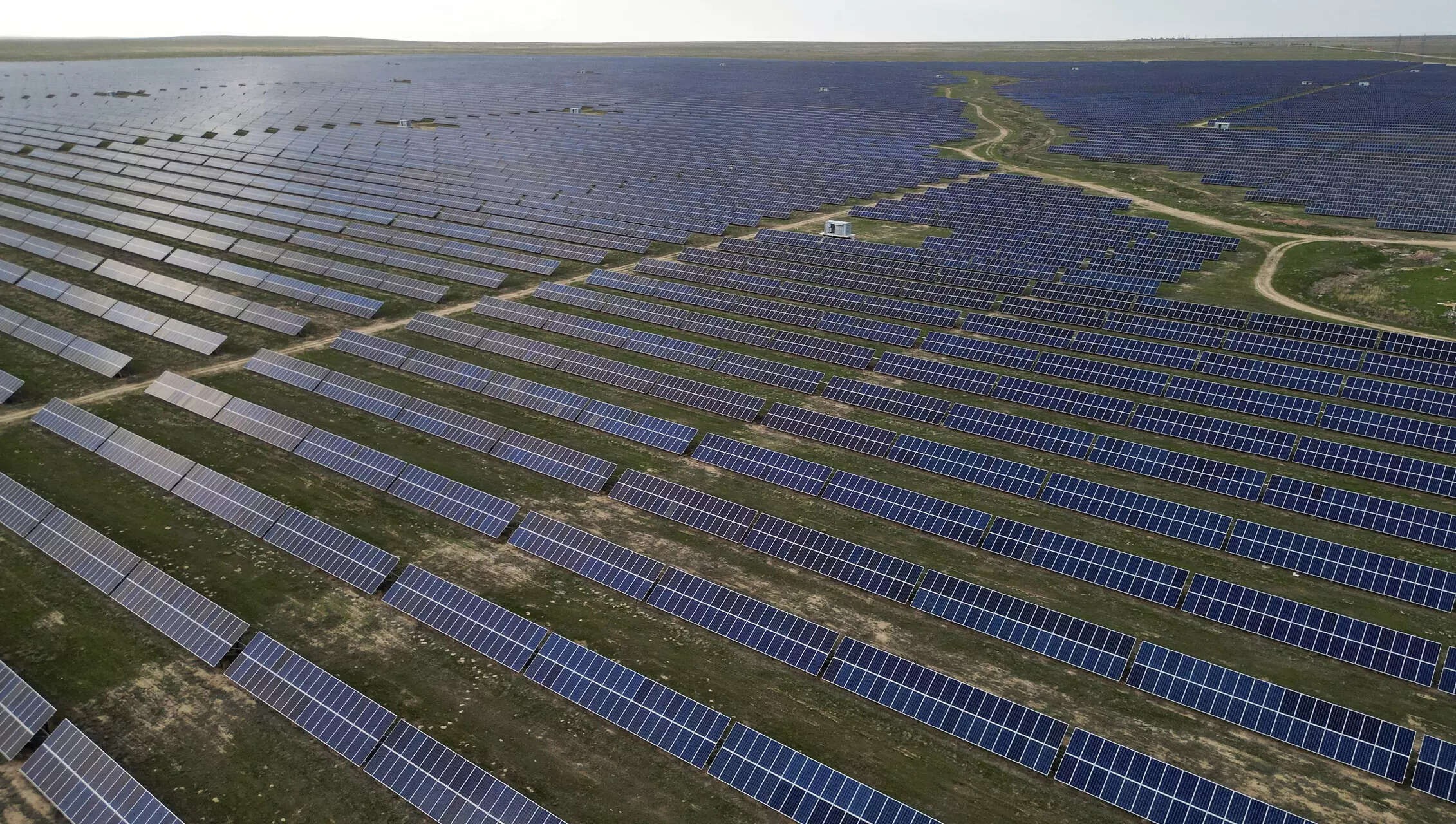

Solar panels rise across India as clean energy takes center stage (Photo: Alamy)
One of the major strategies being adopted is the transition to renewable energy. India has set ambitious targets to increase the share of renewable energy in its energy mix, particularly focusing on solar and wind power.
With the rapid growth of these energy sources, India has become a global leader in renewable energy development. The government is keen on ensuring that renewable energy will provide a portion of the country’s energy needs in the coming years.
Renewable Energy Transition
India’s renewable energy efforts are driven by its long-term vision to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions. The country aims to install 500 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
This ambitious target is part of India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), which were set under the Paris Agreement to limit global warming to below 2°C. The country is focusing heavily on solar energy, as it has one of the largest solar power capacities in the world. The Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) is at the forefront of driving large-scale solar projects across the country.
In addition to solar power, wind energy plays a critical role in India’s renewable energy strategy. India has immense potential for wind power, particularly along its vast coastline.
The government has been supporting the development of wind farms and has been successful in attracting private sector investment to support this transition. By focusing on both solar and wind energy, India is not only reducing its carbon footprint but also creating new economic opportunities and jobs in the clean energy sector.
Adopting Electric Vehicles
Another approach that India is taking to fight climate change is promoting the use of electric vehicles (EVs). The transportation sector is a major contributor to carbon emissions, and India is working to move to cleaner, more sustainable forms of transport.
The government is offering incentives and subsidies to manufacturers and consumers to boost EV adoption. The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme is one such initiative aimed at making electric vehicles more affordable and accessible to the masses.
India’s push for EVs is part of its larger strategy to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and lower air pollution in urban areas. As more people adopt electric vehicles, the demand for petrol and diesel will decrease, helping to reduce carbon emissions from the transport sector. Additionally, the government is investing in the development of EV charging infrastructure, making it easier for people to switch to electric vehicles.
Forest Conservation Efforts
Forest conservation is another crucial aspect of India’s fight against climate change. The country’s forests play a vital role in carbon sequestration, which helps mitigate the impact of climate change.
India has been taking steps to protect and expand its forest cover through afforestation and reforestation programs. These initiatives not only help absorb carbon dioxide but also preserve biodiversity and provide essential resources for local communities.
India’s Green India Mission aims to increase the forest cover in the country and improve the quality of forests. Under this mission, the government is working to restore degraded lands and improve the management of existing forests. The initiative also encourages the planting of trees in urban areas to help reduce the heat island effect and improve air quality.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Sustainable agriculture practices have also gained attention in India’s efforts to address climate change. Agriculture is a key sector in the country, employing a large portion of the population.
However, it is also highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, such as erratic rainfall patterns and rising temperatures. To combat these challenges, India is focusing on climate-resilient agricultural practices, including the use of drought-resistant crops and improved irrigation techniques.
The government has introduced several schemes to support farmers in adapting to climate change. The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) focuses on improving irrigation systems and ensuring water use efficiency.
Additionally, the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) aims to promote the adoption of sustainable farming practices to enhance soil health and increase agricultural productivity.
Water Conservation and Management
Water scarcity is one of the major issues India faces due to climate change. The country has witnessed a reduction in water resources, and this has been exacerbated by erratic weather patterns and over-extraction of groundwater. In response, India has taken steps to improve water conservation and management, particularly in its rural areas.
The Jal Jeevan Mission is one such initiative aimed at providing safe and adequate drinking water to all rural households by 2024. The mission focuses on rainwater harvesting, wastewater treatment, and the construction of water storage facilities.
By improving water management, India hopes to mitigate the impact of water scarcity and ensure that communities have access to clean water even during periods of drought.
Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
India is also focusing on building climate-resilient infrastructure to cope with the impact of extreme weather events. The country is prone to flooding, cyclones, and heatwaves, and it is essential to ensure that infrastructure can withstand such challenges.
The government has launched several initiatives to build climate-resilient infrastructure, including flood-resistant roads, stormwater management systems, and disaster-resilient buildings.
The Smart Cities Mission is one such initiative aimed at building sustainable and climate-resilient urban areas. This program focuses on improving urban infrastructure through the use of technology and innovation.
By promoting the development of smart cities, India is preparing its cities to be more adaptable to the impacts of climate change and is ensuring that urban areas are better equipped to handle environmental challenges.
International Cooperation
India recognizes that climate change is a global challenge that requires collective action. The country has been an active participant in international climate negotiations and has made contributions to global climate action.
India played a key role in the Paris Agreement, where it committed to reducing its carbon intensity and increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy mix.

Turning sunlight and wind into national strength against climate threats (Photo: Getty Images)
Additionally, India has been working with other countries to share knowledge and resources to combat climate change. The International Solar Alliance (ISA), which was launched by India, is a global initiative to promote the use of solar energy and facilitate the sharing of solar technology among member countries. India’s cooperation with international organizations and countries demonstrates its commitment to addressing climate change on a global scale.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite the progress India has made in fighting climate change, several challenges remain. One of the primary challenges is the country’s reliance on coal for electricity generation, which continues to be a source of carbon emissions. While India has made steps in increasing renewable energy capacity, it will take time to fully transition away from coal.
Additionally, India faces challenges in ensuring that climate change policies reach the grassroots level, particularly in rural areas. Many farmers and communities in remote regions are still unaware of the government’s climate adaptation programs and the benefits of sustainable practices.
To address these challenges, India needs to continue its efforts to promote awareness and education on climate change and its impacts. The government should also work closely with local communities to ensure that climate policies are effectively implemented at the grassroots level. Only with continued collaboration and commitment can India achieve its climate goals and contribute to the global fight against climate change.